Increasing Strategies for Salt-Affected Soil Management in Coastal Permaculture
In a bid to combat the challenges posed by climate change and soil salinity in coastal areas, a shift towards sustainable permaculture is gaining momentum. This farming approach, rooted in principles of Earth Care, People Care, and Fair Share, offers a promising solution to create resilient and productive agricultural systems.
Key policy changes are being proposed to support the growth of coastal permaculture. These include implementing targeted coastal erosion management legislation, embedding climate adaptation and resilience into land-use and agricultural policies, and investing in education, training, and community resilience programs. Governments are also recognising the value of sustainable farming practices, such as managing soil salinity, and are encouraging the use of resilient farming practices like agroforestry, cover cropping, and integrated pest management.
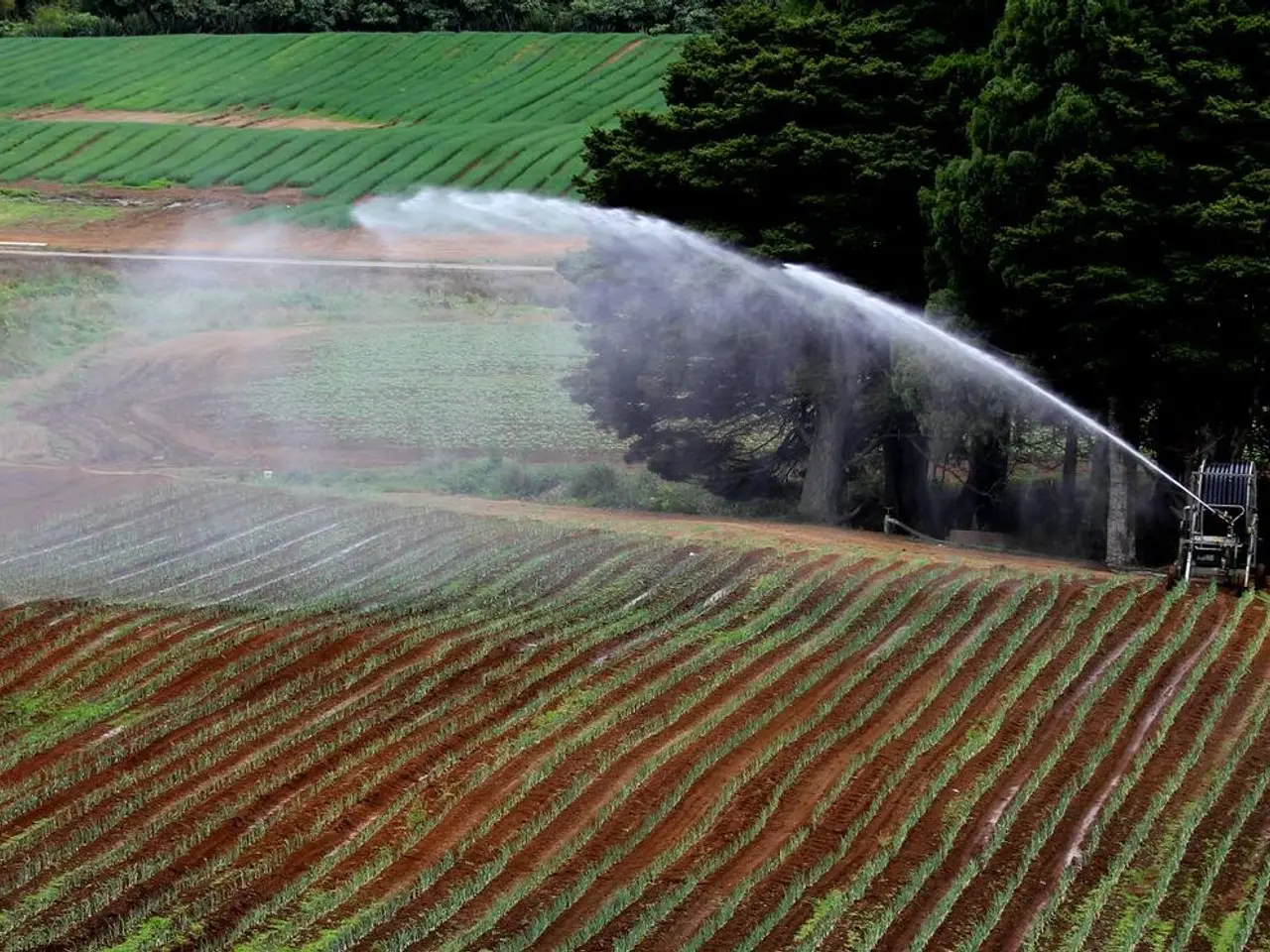
A crucial aspect of coastal permaculture is understanding soil salinity data. This helps in picking the right plants for coastal areas, managing soil and water effectively, and keeping soil healthy, protect water, and support green farming in coastal zones. Using salt-tolerant plants, like halophytes, and techniques such as companion planting and zone planning, are beneficial for coastal agriculture.
Building soil health is essential for coastal permaculture success. Soil microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in soil health, breaking down organic matter, releasing nutrients, and improving soil structure. New farming technologies, like remote sensing and data analytics, help track soil salinity better, enabling farmers to make informed decisions.
Rising sea levels pose a significant threat to coastal areas, bringing saltwater into the soil and threatening crops and ecosystems. To combat this, strategies like using systems such as recirculating aquaculture, creating salt-tolerant crops, and integrating aquaculture with permaculture are being explored. In some places, farmers have switched from rice to shrimp farming due to rising salinity, demonstrating the need for flexible farming methods in coastal areas.
Community involvement is crucial for the success of coastal permaculture projects. In the Khulna and Bagerhat region of Bangladesh, community members have started projects like organic gardens and horticulture sites, showcasing the power of local involvement.
Water management is key for sustainable farming and climate resilience in coastal areas. Rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation are two important methods for this. Drip irrigation sends water straight to plant roots, reducing evaporation, helping control water and salt levels in the soil, and reducing the risk of plant diseases and weeds.
Climate resilience is a key aspect of coastal permaculture, helping coastal communities adapt to sea level rise and extreme weather. Strategies for extreme weather events include using windbreaks, water systems, and planting species that can handle tough weather.
Education and training help residents join in building strong coastal ecosystems. New research and technology are leading to a sustainable future in coastal permaculture, offering hope for communities facing soil degradation challenges. By embracing sustainable permaculture, we can create resilient, productive, and healthy coastal ecosystems for generations to come.
References:
[1] Permaculture Island: https://www.permaculture.co.uk/articles/permaculture-island
[2] Policy Brief: Coastal Permaculture: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328621606_Policy_Brief_Coastal_Permaculture
[3] Education and Training for Coastal Permaculture: https://www.permaculture.org.uk/articles/education-and-training-coastal-permaculture
[4] Integrating Indigenous Knowledge with Permaculture: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328621606_Policy_Brief_Coastal_Permaculture
[5] Sustainable Soil and Water Management for Coastal Permaculture: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328621606_Policy_Brief_Coastal_Permaculture
- The shift towards sustainable permaculture in coastal areas involves growing native plants, following design principles aligned with Earth Care, People Care, and Fair Share.
- Adopting regenerative farming practices, such as companion planting, agroforestry, and integrated pest management, is crucial for sustaining coastal agriculture.
- Community members play a vital role in the success of coastal permaculture projects, demonstrated by initiatives like organic gardens and horticulture sites.
- Soil health improvement is paramount for the success of coastal permaculture, with soil microorganisms being key contributors to this process.
- New farming technologies, like remote sensing and data analytics, aid farmers in managing soil salinity and making informed decisions about farming techniques.
- Building swales and using salt-tolerant plants are effective techniques for maintaining soil and water health in coastal zones.
- In the face of rising sea levels, strategies like recirculating aquaculture and planting salt-tolerant crops are being explored to combat saltwater intrusion.
- Water management in coastal farming is essential for climate resilience, with methods like rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation helping manage water and salt levels effectively.
- Planting species that can handle extreme weather conditions, such as windbreaks, is key for climate resilience in coastal permaculture.
- Education and training programs are vital for empowering residents to contribute to building strong coastal ecosystems.
- New research and technology hold the key to a sustainable future in coastal permaculture, providing hope for communities tackling soil degradation challenges.
- By embracing sustainable permaculture principles, we can create resilient, productive, and healthy coastal ecosystems for future generations.
- Sustainability in coastal permaculture intersects with various domains, including medical-conditions, health-and-wellness, environmental-science, finance, space-and-astronomy, lifestyle, investing, business, personal-finance, technology, education-and-self-development, casino-and-gambling, and sports.
- The weather in coastal areas significantly influences farming practices, and adapting to changing weather patterns is integral to the success of coastal permaculture.